Hello and welcome as we look at non-communicable diseases. We’ll take a look at what they are and some key features about them. Non-communicable diseases are a large group of diseases which are by definition not communicable from one person to another. They’re also called chronic diseases because they're usually long lasting and progress slowly. They occur as a result of a complex interaction of genetic, physiological, behavioral and environmental factors.
Non-communicable
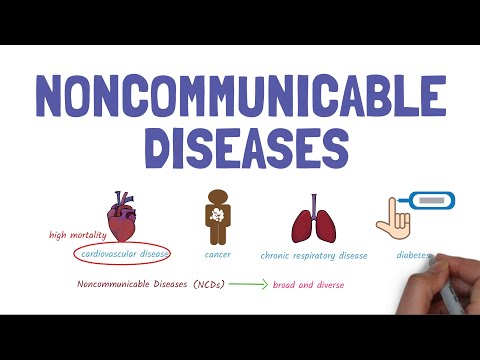
diseases (NCDs) are a very broad and diverse group of diseases and there are
many different types. The four main
types that are responsible for over 80 percent of all deaths are cardiovascular
disease such as heart attacks and strokes, cancer, chronic respiratory
disease such as chronic obstructive
pulmonary diseases, asthma and diabetes. Others include mental health disorders, chronic kidney diseases, musculoskeletal disease
and sensory disorders such as eye
disease or hearing loss . Some of these such as cardiovascular diseases
are large contributors to death and others such as mental health disorders can
have significant health effects due to the disability they cause.
NCDs are a major problem
all over the world and are responsible for about 41 million deaths a year which
is about 71 percent of all deaths. Most of these are in low and middle-income
countries. In addition to this, they cause considerable disability as well. They have a significant economic impact due to
health care and medication costs and because they limit a person's ability to
work. Countries spend a significant
proportion of their health care budgets on these diseases and the problem is
only going to get worse.
It’s estimated that by
2030 deaths from NCDs will increase to 52 million a year this is due to a number
of reasons such as population growth, a rise in aging population,
globalization, urbanization and changes in behavioral occupational
and environmental risk factors.
Non-communicable disease
can affect some groups of people more than others and in different ways. All age groups can be affected by these diseases
for example genetic diseases and some cancers can have an impact from early
childhood. However, NCDs are generally more common in the elderly. This is
because risk factors accumulate over time and the elderly tend to have
co-existing diseases and weakened immune systems. There is an inverse relation
between socioeconomic status and NCDs.
People with low
socioeconomic status are at a higher risk of dying from these diseases and tend
to have more risk factors compared to those with high socioeconomic status. NCDs
and poverty are also closely interrelated. In a vicious cycle, poverty can lead
to increased rates of NCDs and these diseases can drive people into poverty.
RISK FACTORS FOR
NON-COMMUNICABLE DISEASES.
There are many risk
factors that contribute to the development of NCDs and these can vary depending
on the disease but broadly speaking, there are two types of risk factors: non-modifiable
and modifiable.
Non-modifiable
risk factors are those that can't be changed by an individual, these include
age, sex and genetic makeup.
Modifiable
risk factors on the other hand are risk factors that can be changed by a person.
There are four important modifiable risk factors; these are smoking, physical inactivity,
poor nutrition and the harmful use of alcohol. These behavioral risk factors could lead to or
worsen metabolic risk factors such as high blood pressure, high blood lipids,
increased blood glucose and obesity.
It is important to note
that the exposure to risk factors can happen over a person's lifetime. It could
be during childhood, adolescence adulthood, and midlife or even before birth.
During a person's
lifetime, there are critical periods of growth and development when risk
factors can do more damage than they would do at other times and different risk
factors can gradually accumulate over the life course and cause an impact in
later life.
The most important idea is to focus on
reducing risk factors to prevent and control NCDs.
These include reducing smoking through
education, smoking cessation programs, and increasing taxes and prices of
tobacco products, promoting physical activity through media campaigns and
community-based educational programs, promoting healthy diets through actions
such as reducing salt intake, eliminating trans fats, and raising taxes on
sugar sweetened beverages, and reducing the harmful use of alcohol through bans
on advertising, limiting access, increasing taxes enforcing drink driving laws,
and psychosocial interventions.
These strategies go hand in hand with
other preventative strategies such as early screening, effective management of
the disease and managing complications, and addressing the social determinants
of health. Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are a group of diseases that can
lead to either the development of disease or increase a person's susceptibility
to it.
Genes play an important role in the
development or progression of NCDs, and when people are exposed to other risk
factors such as smoking or environmental changes, they may go on to develop a
disease. Epigenetics is an area of active research that is providing insights
on innovative strategies to prevent and control NCDs. Thank you for your continued
readership as we keep learning about health. Keep it here and until next time, it’s
a goodbye for now.
https://youtu.be/BWolWB3tSEU
Nice one
ReplyDeleteHow does this article appear?
ReplyDelete